Composite Technologies
Fiber Finish Systems
The use of the Adherent Technologies’ Axilan® fiber finishes leads to 50-100% improvements in composite strength and stiffness as well as significantly enhancing the environmental durability (including moisture resistance and thermo-oxidative stability) of these composites. The result of these improvements is the potential for expanded use of composites in all arenas of the military, aerospace, industrial, and consumer applications. Adherent Technologies’ fiber finish systems are based on a patent-pending reactive coupling agent (Figure 1) that offers extraordinary compatibility and reactivity with virtually all matrix materials and many carbon and ceramic fibers used in military, aerospace and commercial composite applications.

Schematic of reactive coupling agent function
In contrast to conventional fiber sizings, which are used primarily as handling aids, but do offer some enhanced interaction between the fiber and the matrix material, Adherent Technologies’ fiber finish systems serve primarily to address issues of interfacial bonding by creating direct chemical bonds between the fiber surface and the matrix material while still fulfilling the handling function of conventional sizings. This enhanced adhesion results in more effective load transfer between the fiber and the matrix in the composite, consequently leading to higher strength and stiffness as well as greatly improving moisture resistance by reducing absorption of water and crack propagation at the fiber/matrix interface.
The ability to achieve these higher mechanical properties is fundamentally important to the development of lighter, more efficient composite structures, which can in turn lead to greater agility, reduced deployment costs, and lower radar signatures, among other benefits. It is critical to note that the reactive coupling agent that is the heart of the fiber finish system is extremely versatile and can be used in conjunction with virtually any common matrix material used in carbon fiber reinforced composites. Matrix materials evaluated to date include vinyl ester, epoxy, phenolic, bismaleimide, and polyimide. This versatility offers enhanced compatibility and composite capability.
This technology is intended to replace the current commercial fiber sizing with a fiber finish that is 100% compatible with matrix resin, does not result in significant processing problems, and increases the resulting composite mechanical properties to near theoretical values.
Adherent Technologies’ Finish Features, Advantages, and Benefits
| Features | Advantages | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Customized to desired matrix resin | Improved wetting and matrix compatibility | Reduced processing cost |
| Reactive finish | Chemical bond across fiber/matrix interface | 50-100% improvement in composite strength and stiffness, enhanced environmental durability |
| Water based process resulting in no VOC emissions and no flammability | Direct integration with existing manufacturing lines | Low cost, low risk, quick to market process. |
| Reactive coupling agent | Extremely versatile material | Works with most composites so can be used on many carbon fiber product platforms |
High-Temperature Finishes for Polyimide Matrix Composites
Adherent Technologies has recently developed a new finish system for carbon/polyimide composites to improve interface dependent properties and durability. High-temperature finish systems consisting of a reactive coupling agent, polyimide carrier, and solvent were developed. The reactive coupling agents have been shown to chemically bond to carbon fibers in prior work. An aqueous based finish was also developed by synthesizing a water soluble coupling agent and polyimide.
Unidirectional composite laminates were prepared from prepreg made with different ATI finish formulations, a commercial high-temperature sizing, and unsized carbon fiber. The laminates were processed with autoclave molding at 371°C (700°F) followed by an air circulating oven postcure at 399°C (750°F). Mechanical testing data is discussed below:
Dry Samples
Room temperature dry – similar for all fiber surface chemistries. The laminates with the finished fibers did show two times higher fracture toughness in interface sensitive tests (transverse flexure, short beam shear, compression).
| Longitudinal (0°) Flexural Strength | 260 ksi |
| Transverse (90°) Flexural Strength | 24 ksi |
| Short Beam Shear Strength | 16 ksi |
| Compression Strength | 145 ksi |
At 550°F in the dry condition the finished material is twice as strong and has 2-3 times the modulus and toughness compared to the commercially sized material in transverse flexure.
Moisture-Aged Samples
- Reactive finished reduce the moisture absorption rate under elevated temperature and humidity conditions
- 30% higher strength than commerically sized fiber
- 400% higher toughness than commercially sized fiber.
Failure analysis using scanning electron microsocope (SEM) techniques showed the strength and toughness increases were due to superior interfacial bonding that lead to increased plastic deformation in the matrix.




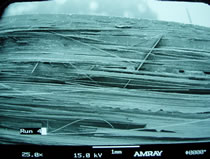
SEM photomicrographs of 90° failure surfaces of moisture saturated laminates with commercial sizing (left) and 1.0% reactive finish (right). The flatter fracture surface observed for the commercially sized sample (upper left) relative to that for the reactive finish (upper right) is indicative of lower energy absorption and a lower fracture toughness. At higher magnifications, more bare fibers are apparent on the commercially sized laminate (lower left) than the 1.0% reactive finished laminate (lower right). In addition, more plastic deformation in the matrix resin is seen with the reactive finished laminate.
Thermally Aged Samples
Accelerated Testing:
- 36% lower weight loss relative to commercially sized material
- 20% higher strength relative to commercially sized material
Long term aging at 600°F (1000 hr, tested @ 550°F):
- 20-40 percent better strength and toughness retention in longitudinal and transverse flexure
Reactive Finish Systems for Carbon/Vinyl Ester Composites
Adherent Technologies has developed a reactive finish system that is compatible with carbon/vinyl ester composites that traditionally have difficulties in meeting theoretical performance targets. In contrast to conventional fiber sizings, ATI’s reactive finish systems offer direct chemical bonding between both the fiber and the matrix material of the composite through a proprietary reactive coupling agent. The use of the Adherent Technologies’ fiber finishes leads to 50–100% improvements in composite strength and stiffness as well as significantly enhancing the environmental durability (including moisture resistance and thermo-oxidative stability) of these composites.
In these programs, unidirectional laminates containing several types of fiber surfaces (unsized, commercially sized, and reactive finishes of varying formulations) were prepared, characterized for microstructure, and mechanically tested using interface sensitive test methods (transverse flexure, short beam shear) and a fiber dominated test (longitudinal flexure), and characterized for failure mode. Data are summarized in the following tables.
Table I. Longitudinal (0°) Flexural Properties of Carbon/Vinyl Ester Wet Wound Laminates
| Laminate Type | Ultimate Strength (psi) | Young's Modulus (psi) | Deflection at Failure (in.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsized | 139,211 ± 7.0% | 15,192,700 ± 4.7% | 0.202 ± 4.6% |
| Commercial Size | 152,623 ± 8.9% | 15,113,900 ± 9.3% | 0.205 ± 4.0% |
| ATI VE Finish 137B | 133,652 ± 21.6% | 12,769,800 ± 26.8% | 0.209 ± 7.3% |
| ATI VE Finish 139A1 | 143,914 ± 4.3% | 14,495,000 ± 1.1% | 0.199 ± 8.5% |
| ATI VE Finish 139A2 | 164,683 ± 5.1% | 14,729,900 ± 3.3% | 0.237 ± 3.4% |
| ATI VE Finish 142A | 163,520 ± 1.5% | 14,073,800 ± 1.8% | 0.235 ± 4.3% |
Table II. Transverse (90°) Flexural Properties of Carbon/Vinyl Ester Wet Wound Laminates
| Laminate Type | Ultimate Strength (psi) | Young's Modulus (psi) | Deflection at Failure (in.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsized | 3,541 ± 6.9% | 584,017 ± 8.6% | 0.007 ± 6.9% |
| Commercial Size | 3,359 ± 6.8% | 622,058 ± 12.4% | 0.006 ± 11.6% |
| ATI VE Finish 137B | 8,715 ± 6.2% | 778,074 ± 4.6% | 0.014 ± 9.4% |
| ATI VE Finish 139A1 | 10,726 ± 7.1% | 925,625 ± 4.2% | 0.014 ± 6.3% |
| ATI VE Finish 139A2 | 8,672 ± 13.3% | 804,847 ± 2.6% | 0.012 ± 14.4% |
| ATI VE Finish 142A | 10,813 ± 4.5% | 814,711 ± 4.6% | 0.015 ± 3.5% |
Table III. Short Beam Shear Properties of Carbon/Vinyl Ester Wet Wound Laminates
| Laminate Type | Shear Strength (psi) | Standard Deviation (psi) | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsized | 6,801 | 310 | 4.6 |
| Commercial Size | 7,364 | 403 | 5.5 |
| ATI VE Finish 137B | 8,748 | 125 | 1.4 |
| ATI VE Finish 139A1 | 8,531 | 95 | 1.1 |
| ATI VE Finish 139A2 | 9,699 | 143 | 1.5 |
| *ATI VE Finish 139A2 | 10,681 | 153 | 1.4 |
| *ATI VE Finish 142A | 12,219 | 171 | 1.4 |
Results show that the reactive finishes substantially improve the carbon/vinyl ester interface-dominated mechanical properties compared to the unsized or commercially sized materials. In addition, the toughness of the interface in shear as seen in the area under the load-deflection curves is substantially increased.
Failure mode analysis shows that interfacial failure dominates the unsized and commercially sized materials, whereas resin cohesive failure dominates the ATI finished materials. This is a strong indication that the desired chemical bonding is occurring at the carbon/vinyl ester interface through the reactive finish.
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Unsized | Commercially sized | Reactive finished |
